Organic farming, while often praised for its environmental benefits, may have negative consequences for The environment & crop yields. Organic farmers typically use natural fertilizers, such as compost or manure, instead of synthetic ones, which can result in nutrient imbalances in The soil & lower crop yields. Additionally, organic farming often requires larger land areas To produce The same amount of food as conventional farming, leading To deforestation & habitat loss. Furthermore, organic farming practices, such as crop rotation & reliance on natural predators, may not always be effective in controlling pests & diseases, resulting in lower crop quality & quantity.
Why Organic Farming May Have Negative Consequences for the Environment and Crop Yields. Discover The hidden side of organic farming! Explore why it might harm The environment & reduce crop yields. Uncover The surprising truths behind this trendy practice.
Why Organic Farming May Have Negative Consequences for The Environment & Crop Yields
Organic farming has gained popularity in recent years due To its perceived environmental benefits & healthier produce. However, despite its positive image, organic farming may have negative consequences for The environment & crop yields. In this article, we will explore some of The potential drawbacks of organic farming practices.
One of The main concerns with organic farming is its lower crop yields compared To conventional methods. Organic farmers rely on natural fertilizers & pest control methods, which can be less effective in preventing crop damage. This often leads To lower productivity & higher production costs. Studies have shown that organic farms can produce up To 30% less food than conventional farms, making it difficult To meet growing global food demands.
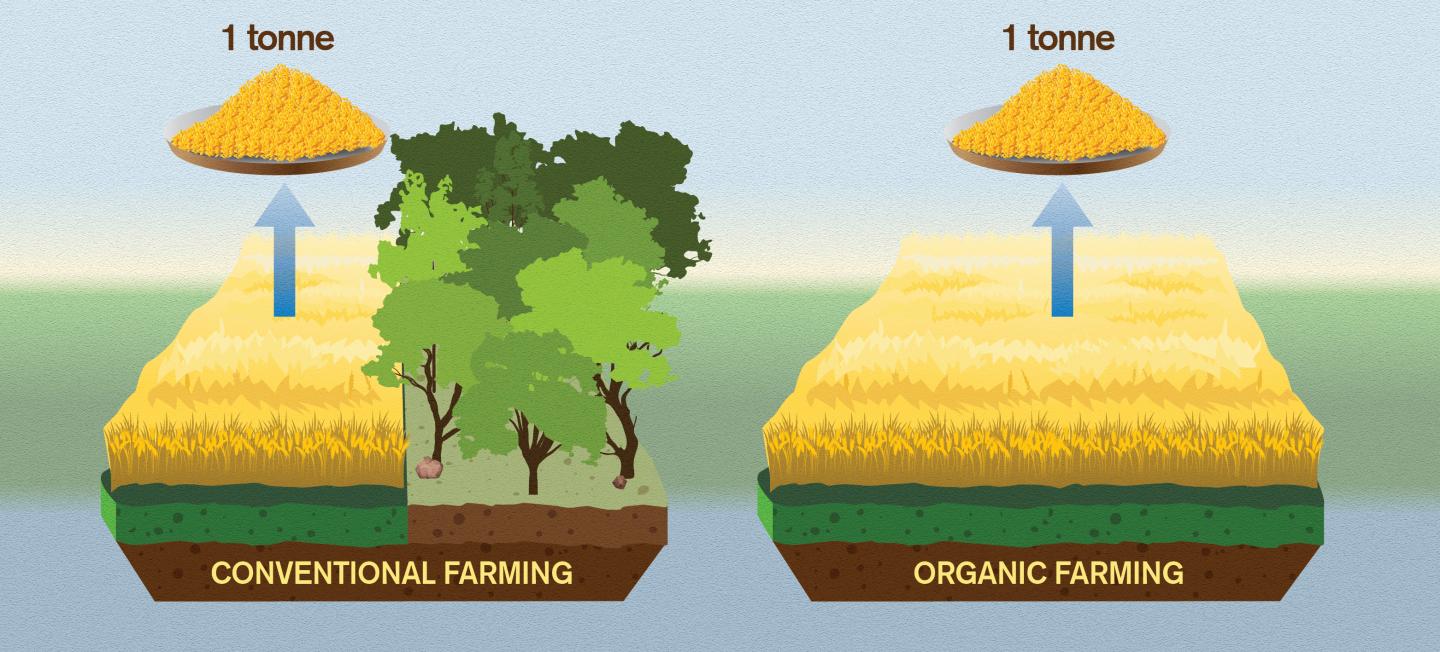
Another issue with organic farming is its impact on The environment. While organic practices aim To minimize The use of synthetic pesticides & fertilizers, they often require large amounts of land To compensate for lower crop yields. This expansion of agricultural land can lead To deforestation, habitat destruction, & loss of biodiversity. Additionally, organic farms may use more water & produce more greenhouse gas emissions per unit of yield compared To conventional farms.
Impact on Soil Health
Organic farming practices, such as The avoidance of synthetic fertilizers & pesticides, can have both positive & negative effects on soil health. While organic methods promote The development of beneficial microorganisms & improve soil structure, they may also lead To nutrient imbalances & decreased soil fertility over time. Without The use of synthetic fertilizers, organic farmers rely heavily on organic matter & cover crops To replenish nutrients in The soil. However, this process can be slow & may not provide adequate nutrient levels for optimal crop growth.
Moreover, organic farming often requires more tillage To control weeds, which can contribute To soil erosion & degradation. Excessive tillage can disrupt soil structure, increase The risk of nutrient runoff, & decrease water retention capacity. These effects can negatively impact soil health & reduce long-term agricultural productivity.
Although organic farming aims To minimize chemical inputs, it is important To note that organic pesticides & fertilizers can still pose risks To The environment & human health. While these substances may be derived from natural sources, they can still have negative impacts on non-target organisms & contaminate water sources if not used properly.
Food Security & Affordability
As mentioned earlier, organic farming generally yields lower crop production compared To conventional methods. This limitation raises concerns about food security, especially in regions with limited agricultural resources. With a growing global population, it is crucial To produce enough food To meet The dietary needs of everyone. The lower productivity of organic farming may result in higher food prices, making organic produce less accessible & affordable for lower-income populations.
Lack of Synthetic Input Innovation
One potential drawback of organic farming is The limited availability of synthetic inputs, such as genetically modified organisms (GMOs) & certain pesticides. While these inputs are controversial due To concerns about their long-term effects on health & The environment, they have also contributed To increased crop yields & pest resistance management in conventional farming. By restricting The use of such inputs, organic farming may limit its ability To adopt new technologies & innovations that could address some of its current limitations.
Reduced Profitability for Farmers
Organic farming often requires higher labor & management inputs To maintain soil health, manage pests, & control weeds organically. These additional costs can reduce The profitability of organic farming operations, especially for small-scale farmers. Conventional farming practices that utilize synthetic inputs & machinery may be more financially sustainable for farmers, allowing them To invest in their operations & improve their livelihoods.
Features of Organic Farming with Potential Negative Consequences
- Reduced crop yields compared To conventional farming methods 🤔
- Increased land requirements & potential for deforestation 🌲
- Possible negative impacts on soil health & fertility 🧊
- Use of organic pesticides & fertilizers with potential environmental & health risks 🐛
- Challenges in achieving food security & affordability 🍲
- Lack of access To synthetic inputs & potential limitations on adopting new technologies 🛠
- Potential reduced profitability for farmers, especially for small-scale operations 💰
Considering The potential negative consequences of organic farming on The environment, crop yields, & food security, it is important To approach The debate around organic versus conventional farming with a balanced perspective. While organic farming can offer certain benefits, it is essential To explore ways To mitigate its drawbacks & develop sustainable agricultural practices that prioritize both environmental protection & food production.
The Future of Organic Farming
Efforts are underway To address some of The challenges associated with organic farming & improve its sustainability. Research is focused on developing innovative organic farming practices that optimize nutrient management, pest control, & soil health. Additionally, advancements in technology, such as precision agriculture & agroecology, aim To improve The efficiency & productivity of organic farming.
It is worth noting that a combination of organic & conventional farming practices, known as integrated pest management (IPM), may offer a more balanced approach. IPM combines The use of biological control methods, organic pesticides, & targeted synthetic inputs To minimize environmental damage while ensuring optimal crop yields & food security.
In conclusion, while organic farming has its merits, it is crucial To acknowledge The potential negative consequences it may have for The environment & crop yields. Balancing environmental sustainability, food production, & affordability will require ongoing research, innovation, & collaboration between organic & conventional farming practices.
Organic farming has gained popularity in recent years due To its perceived benefits for The environment & human health. However, there is growing evidence that organic agriculture may not be as environmentally friendly as previously thought. This article will explore some of The negative consequences that organic farming can have on The environment & crop yields.
The Impact on Soil Health
One of The main principles of organic farming is To promote soil health & fertility through natural methods. However, The use of organic fertilizers, such as manure, can lead To nutrient imbalances in The soil. These imbalances can result in excessive nutrient runoff into nearby water bodies, leading To water pollution & The eutrophication of ecosystems.
Additionally, organic farming practices often involve tilling The soil, which can lead To soil erosion & degradation. The constant disturbance of The soil can disrupt its natural structure & reduce its ability To hold water & nutrients. This, in turn, can negatively affect crop yields & overall soil health.
Pest & Weed Control Challenges
Organic farming relies heavily on natural methods of pest & weed control, such as The use of beneficial insects & crop rotation. While these methods can be effective, they may not provide adequate protection against pests & weeds, especially in large-scale agriculture.
Conventional farming, on The other hand, utilizes synthetic pesticides & herbicides that can help control pests & weeds more effectively. While The use of these chemicals can have negative environmental impacts, such as water pollution & harm To non-target organisms, they also play a crucial role in ensuring high crop yields & protecting food security.
Resource Demands & Land Use
Organic farming typically requires more land compared To conventional agriculture To achieve The same level of crop yields. This increased land use can lead To deforestation & habitat loss, contributing To biodiversity decline.
Furthermore, organic farming often requires more manual labor & resources, such as water, To maintain The crops & soil health. This can make organic agriculture less economically viable for small-scale farmers without access To sufficient resources & labor.
To better understand The potential negative consequences of organic farming on The environment & crop yields, let’s compare some key factors between organic & conventional agriculture.
| Factors | Organic Farming | Conventional Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Soil Health | Relies on organic fertilizers & natural methods | Utilizes synthetic fertilizers & pesticides |
| Pest & Weed Control | Natural methods with potential limitations | Synthetic pesticides & herbicides for better control |
| Land Use | Requires more land To achieve equivalent yields | Utilizes less land due To higher crop yields |
The Role of Technology
Advances in technology, such as genetic engineering & precision agriculture, have enabled conventional farming To become more sustainable & environmentally friendly. Genetically modified crops can be engineered To be resistant To pests & diseases, reducing The need for synthetic pesticides. Precision agriculture allows for targeted & efficient use of inputs, optimizing resource utilization & minimizing environmental impacts.
While organic farming may be perceived as a more environmentally friendly option, it is essential To consider its potential negative consequences on soil health, pest & weed control, resource demands, & land use. Conventional farming, with The aid of technology, has made significant strides in mitigating its environmental impacts & ensuring high crop yields. It is crucial To continue developing sustainable farming practices that balance environmental concerns with food security needs.
Why Organic Farming May Have Negative Consequences for The Environment & Crop Yields
Organic farming, although often praised for its eco-friendly approach, can potentially have negative consequences for both The environment & crop yields. Here are some points To consider:
Soil Erosion
The use of organic farming methods often involves tilling The soil To control weeds, which can increase The risk of soil erosion. When The soil is exposed through tilling, it becomes more susceptible To wind & water erosion, leading To The loss of topsoil & essential nutrients.
Pest Control Challenges
Organic farming relies heavily on natural pest control methods, such as crop rotation & biological pest control, which may not always effectively combat pests. Unlike conventional farming, The use of synthetic pesticides is limited in organic farming, making it more challenging To manage pest outbreaks & prevent crop damage.
Lower Crop Yields
Due To The limited availability of synthetic fertilizers & pesticides, organic farming may experience lower crop yields compared To conventional farming methods. Organic farmers often face difficulties in providing crops with sufficient nutrients & protecting them against pests, ultimately affecting The overall yield & productivity of their farms.
Land Requirement
Organic farming generally requires more land compared To conventional farming To achieve similar yields. This can be attributed To The need for crop rotation, larger buffer zones, & The integration of livestock in organic systems. The increased land requirement for organic farming can put additional pressure on natural habitats & lead To deforestation or habitat destruction.
Transportation & Distribution Challenges
Organic farming often involves smaller-scale production & distribution systems, which can result in increased transportation distances for organic products. This transportation can contribute To carbon emissions & other negative environmental impacts associated with long-distance travel.
Economic Viability
Organic farming can be more labor-intensive & expensive compared To conventional farming, putting financial strain on farmers. The costs associated with organic certification, organic fertilizers, pest control methods, & marketing can make organic farming economically challenging for some farmers, potentially discouraging its widespread adoption.
Conclusion
While organic farming offers significant benefits, it is crucial To acknowledge its potential negative consequences for The environment & crop yields. Effective management practices & continuous research are necessary To mitigate these drawbacks & maximize The sustainability & productivity of organic farming systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while organic farming is often touted as a sustainable & environmentally friendly practice, it may have negative consequences for both The environment & crop yields. By avoiding The use of synthetic fertilizers & pesticides, organic farming may lead To decreased soil fertility & increased vulnerability To pests & diseases. This can result in lower crop yields, potentially leading To food shortages & economic losses.
Furthermore, organic farming requires larger land areas To produce The same amount of food as conventional farming methods. This can lead To deforestation & The loss of natural habitats for countless species. Additionally, The increased land & resource requirements of organic farming can also contribute To higher greenhouse gas emissions, further exacerbating climate change.
While The principles behind organic farming are admirable & there is evidence that it has certain benefits such as improved soil health & reduced chemical runoff, it is crucial To weigh these against The potential negative consequences. As consumers, it is important To be aware of The trade-offs involved in choosing organic produce & consider The broader environmental impact of our food choices.
Ultimately, a holistic approach that combines The best practices of organic & conventional farming may be necessary To achieve sustainable agriculture. This would involve utilizing organic farming techniques where appropriate, such as improving soil health through crop rotation & composting, while also making use of synthetic inputs & genetically modified crops To enhance productivity & reduce environmental impact.
In conclusion, while organic farming has its merits, it is important To critically evaluate its potential negative consequences for The environment & crop yields. By continuing To research & innovate in The field of agriculture, we can strive towards a more sustainable & balanced approach To feeding our growing population while also protecting our planet.