Organic farming stands apart from conventional farming due To its focus on sustainable & natural practices. Unlike conventional farming, which heavily relies on synthetic pesticides & fertilizers, organic farming emphasizes The use of organic materials like compost & animal manure To nourish The soil. In organic farming, genetically modified organisms & growth hormones are strictly prohibited, ensuring The production of chemical-free & non-GMO crops. Moreover, organic farmers prioritize biodiversity, crop rotation, & soil conservation To enhance soil health & promote ecological balance. These practices not only provide consumers with healthier & more nutritious food but also contribute To The overall preservation & sustainability of The environment.
What Sets Organic Farming Apart from Conventional Farming?. Discover The key differences between organic farming & conventional farming. Learn why organic farming stands out, using sustainable practices & avoiding harmful chemicals. Explore The benefits of choosing organic for a healthier & more eco-friendly future.
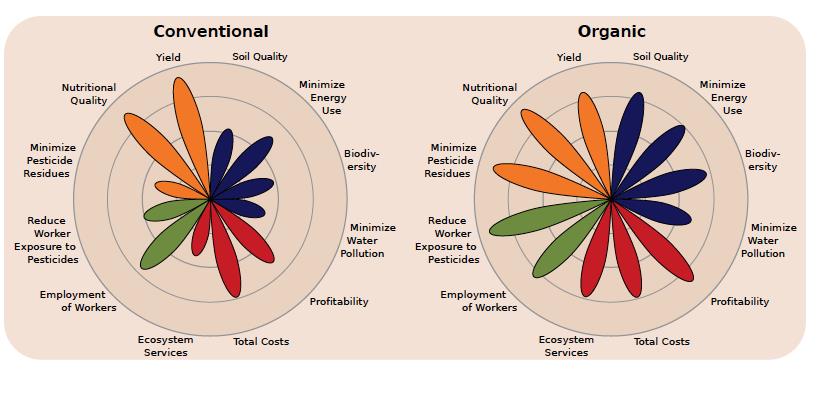
The Benefits of Organic Farming
Organic farming has become increasingly popular in recent years, as more & more people are becoming aware of The benefits it offers. But what exactly sets organic farming apart from conventional farming? In this article, we will explore The key aspects of organic farming that make it a sustainable & environmentally friendly choice.
Environmental Impact
One of The main differences between organic & conventional farming lies in their approach To The environment. Organic farming practices aim To minimize The use of artificial chemicals & instead focus on natural methods of pest control & soil fertility. This helps To reduce pollution & minimize The impact on ecosystems.
Furthermore, organic farms often prioritize biodiversity by creating habitats for wildlife & preserving natural resources, such as water & soil. This holistic approach To agriculture contributes To The overall health of The environment & helps To protect fragile ecosystems.
Health Benefits
Another important aspect of organic farming is its focus on producing healthier & more nutritious food. Organic crops are grown without The use of synthetic pesticides, herbicides, & genetically modified organisms (GMOs). This means that consumers who choose organic products can reduce their exposure To potentially harmful chemicals.
Several studies have also suggested that organic crops contain higher levels of certain nutrients, such as vitamins & antioxidants. For example, a study published in The Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry found that organic strawberries had higher levels of vitamin C & antioxidants compared To conventionally grown strawberries.
Economic Sustainability
While organic farming may initially require more labor & investment, it can also lead To long-term economic sustainability. Organic farms often have lower input costs since they don’t rely on expensive synthetic fertilizers & pesticides. Additionally, organic products often command a premium price in The market, which can provide farmers with higher returns.

Moreover, organic farming promotes local & small-scale agriculture, contributing To vibrant rural communities & reducing dependence on imported food. By supporting organic farming, consumers can help create a more sustainable & resilient food system.
Farmers’ Well-being
Conventional farming practices often involve The use of synthetic chemicals that can be harmful To farmers’ health. Prolonged exposure To pesticides & fertilizers has been linked To various health issues, including respiratory problems, skin disorders, & even cancer.
In contrast, organic farmers work with nature & minimize their exposure To toxic substances. By reducing chemical inputs & adopting organic farming practices, farmers can create a safer working environment for themselves & their employees.
Innovation in Organic Farming
As The demand for organic products continues To grow, so does The need for innovation in organic farming practices. Farmers & researchers are constantly exploring new techniques & solutions To improve organic farming methods, such as organic pest management strategies, crop rotation, & soil conservation practices.
Through research & development, organic farming can continue To evolve & become even more efficient & sustainable. This ongoing commitment To innovation is vital in ensuring that organic farming remains a viable & scalable solution for feeding our growing population.
Organic farming: A sustainable approach To agriculture
Organic farming has gained significant attention in recent years due To its sustainable & environmentally friendly practices. Unlike conventional farming, which relies heavily on synthetic chemicals & genetically modified organisms (GMOs), organic farming focuses on natural methods To promote soil health, enhance biodiversity, & minimize environmental impact. This section will explore The fundamental differences between organic & conventional farming methods.
The principles of organic farming
Organic farming is guided by several principles that differentiate it from conventional agriculture. These principles include:
- Promoting soil health: Organic farmers prioritize soil fertility through The use of compost, cover crops, & crop rotation. These practices enhance soil structure, water retention, & nutrient availability.
- Protecting biodiversity: Organic farming encourages The preservation of diverse plant & animal species. By avoiding synthetic pesticides & herbicides, organic farmers create habitats that support a wide range of beneficial insects, birds, & other wildlife.
- Avoiding synthetic inputs: Organic farmers eliminate The use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, & GMOs. Instead, they rely on natural alternatives such as compost, crop rotation, & biological pest control methods.
- Promoting animal welfare: Organic farming places a strong emphasis on animal welfare. Livestock must have access To outdoor areas, receive organic feed, & are not administered growth hormones or antibiotics.
Section 2: Benefits of Organic Farming
1. Environmental benefits
Organic farming has several environmental benefits that set it apart from conventional agriculture:
- Reduced chemical pollution: By eliminating synthetic pesticides & fertilizers, organic farming helps To minimize water & soil pollution. This protects aquatic ecosystems & promotes The health of pollinators, such as bees & butterflies.
- Conservation of natural resources: Organic farming practices, such as cover cropping & mulching, help To conserve water, reduce soil erosion, & improve soil quality. This promotes long-term sustainability & resilience in agricultural systems.
- Enhanced biodiversity: Organic farms support a greater diversity of plant & animal species compared To conventional farms. This is due To The absence of chemical inputs & The provision of habitats for beneficial organisms.
2. Health benefits
Consuming organic products can have potential health benefits:
- Reduced pesticide exposure: Organic farming prohibits The use of synthetic pesticides, reducing The risk of pesticide residues on crops & potential health hazards associated with pesticide exposure.
- Higher nutrient content: Some studies suggest that organic crops may contain higher levels of certain nutrients compared To conventionally grown crops. However, more research is needed To fully understand these differences.
- Absence of GMOs: Organic farming prohibits The use of genetically modified organisms, providing consumers with a GMO-free choice.
Section 3: Challenges & Limitations
1. Yield limitations
One of The challenges of organic farming is its lower yields compared To conventional methods. Without The use of synthetic fertilizers & pesticides, organic farmers often face greater pest & weed pressures, leading To lower crop productivity in some cases. However, with proper management practices, organic farmers can achieve competitive yields.
2. Transition period
Transitioning from conventional To organic farming requires a significant investment of time & resources. During The transition period, which can take several years, farmers must adhere To organic practices without benefiting from The higher prices of certified organic products. This financial strain can discourage some farmers from making The switch.
3. Certification process
Organic farmers must meet strict certification standards To label their products as organic. This involves rigorous inspections, record-keeping, & compliance with organic regulations. The certification process can be time-consuming & costly for small-scale farmers.
Section 4: Organic Farming vs. Conventional Farming
Comparison table
Here is a comparison table highlighting The key differences between organic farming & conventional farming:
| Aspect | Organic Farming | Conventional Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Use of synthetic chemicals | Minimized | Extensive |
| Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) | Prohibited | Allowed |
| Soil health | Emphasized through organic matter & natural fertilizers | Dependent on synthetic fertilizers |
| Biodiversity | Promoted through habitat preservation | May be compromised due To chemical use |
| Animal welfare | High standards of animal welfare | Varies depending on farming practices |
Section 5: Conclusion
In conclusion, organic farming offers numerous advantages over conventional farming. Its sustainable practices help protect The environment, conserve natural resources, & promote healthier food choices. While there are challenges & limitations associated with organic farming, its positive impact on both human health & The planet makes it an increasingly popular choice for farmers & consumers alike.
Personally, I have had The opportunity To work on an organic farm, & it was a transformative experience. Being able To nurture The soil, witness The diversity of life thriving in The fields, & contribute To a more sustainable food system was incredibly rewarding.
If you’re interested in learning more about organic farming, I encourage you To visit The Rodale Institute & The Organic Produce Network for further information.
Remember, by supporting organic farming practices, you play a vital role in preserving The planet & promoting a sustainable future for generations To come.

What sets organic farming apart from conventional farming?
Organic farming & conventional farming differ in several key ways:
What are The main principles of organic farming?
Organic farming is based on The following principles:
Is organic farming better for The environment?
Yes, organic farming has several environmental benefits:
Does organic farming use pesticides?
Yes, organic farming utilizes natural pesticides:
Are there any advantages To conventional farming?
Conventional farming does have a few advantages:
How does organic farming benefit human health?
Organic farming can positively impact human health through:
What certifications are required for organic farming?
To be considered organic, farmers must obtain certain certifications:
Can organic farming feed The world’s growing population?
Yes, organic farming has The potential To feed The world’s population:
What challenges does organic farming face?
Organic farming does encounter a few challenges:
Is organic farming more expensive than conventional farming?
Yes, organic farming can be more expensive due To:
Conclusion
In conclusion, organic farming stands apart from conventional farming in several remarkable ways. With a focus on sustainability, organic farming promotes biodiversity, conserves natural resources, & minimizes environmental pollution. By avoiding synthetic fertilizers & pesticides, organic farmers prioritize The health & well-being of both consumers & The planet. Additionally, organic farming practices prioritize animal welfare, promoting The humane treatment of livestock.
Not only does organic farming produce food that is free from potentially harmful chemical residues, but it also offers nutritional benefits. Studies have shown that organic crops tend To have higher levels of certain nutrients & antioxidants, which can help boost our overall health. Furthermore, The avoidance of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) in organic farming ensures that consumers have access To non-engineered & non-altered natural produce.
While organic farming may face challenges such as higher costs & lower yields compared To conventional farming, its benefits outweigh these drawbacks. By supporting organic farming, consumers can contribute To a healthier environment, promote sustainable agriculture, & prioritize their own well-being. Remember, The food choices we make have a significant impact not only on our own health but also on The health of The planet we all call home.