Organic farming offers numerous advantages such as The absence of synthetic pesticides & fertilizers, reduced environmental impact, improved soil health, & increased biodiversity. On The other hand, conventional farming provides higher yields, lower production costs, & greater efficiency in terms of resources. However, it is associated with potential pollution & health risks due To The use of chemicals. Both methods have their own set of pros & cons, & The choice ultimately depends on factors like consumer preferences, environmental impact, & economic viability.
The Pros and Cons of Organic vs Conventional Farming: A Comparative Analysis. Confused about organic & conventional farming? Discover The advantages & disadvantages in our comparative analysis. No jargon, just plain & simple language. Explore The pros & cons today!
The Pros & Cons of Organic vs Conventional Farming: A Comparative Analysis
Organic & conventional farming methods have been widely debated in recent years. With concerns over sustainability, environmental impact, & food safety, it is important To understand The pros & cons of each approach. This comparative analysis will delve into The key aspects of organic & conventional farming, highlighting their advantages & disadvantages. By examining these factors, individuals can make informed choices regarding The food they consume & support.
The Pros of Organic Farming
1. Environmental Sustainability
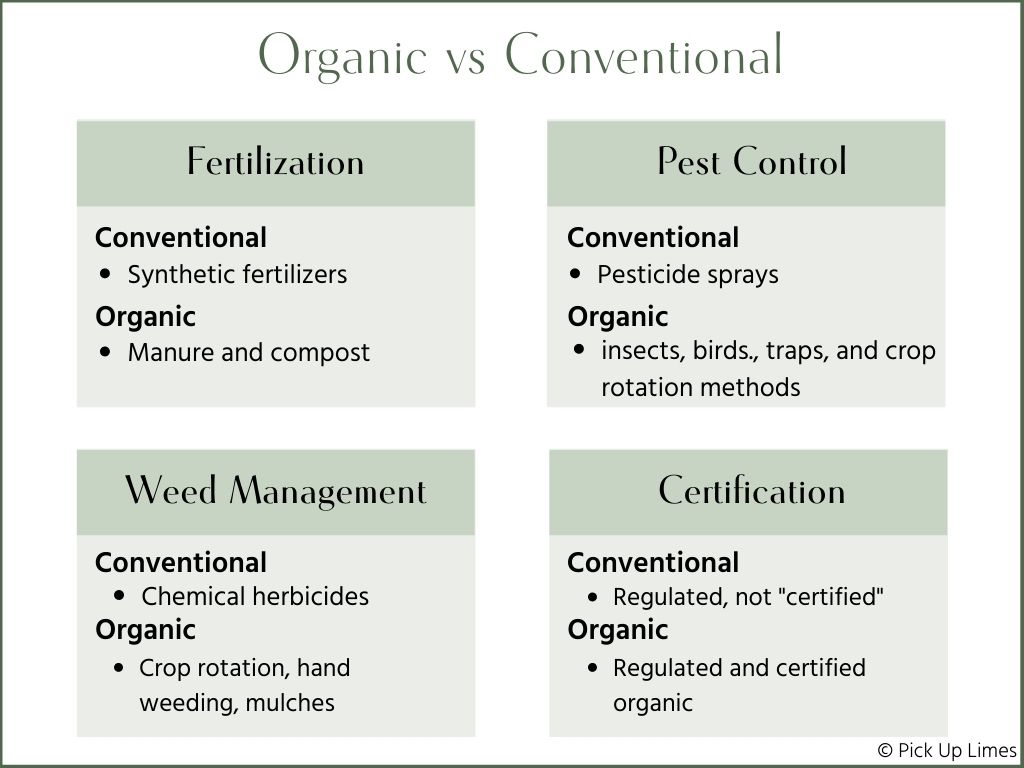
Organic farming practices prioritize The use of natural fertilizers & pest control methods, reducing The reliance on harmful chemicals. This approach promotes soil health, biodiversity, & overall ecosystem balance. Additionally, organic farms often implement methods such as crop rotation & cover cropping To enhance soil fertility & reduce erosion.
2. Improved Food Quality
Organic farming prohibits The use of synthetic pesticides, GMOs, & growth hormones in livestock. This means that organic produce & animal products are free from harmful residues, making them a safer & healthier choice for consumers. Organic farming can also enhance The nutritional value of food, as organic crops tend To contain higher levels of certain vitamins, minerals, & antioxidants.
3. Protecting Animal Welfare
Organic farming standards prioritize The well-being of animals. Livestock raised organically are provided with access To outdoor areas, given organic feed, & are not subjected To routine use of antibiotics or growth hormones.

This approach promotes more humane treatment of animals & supports their natural behaviors.
The Cons of Organic Farming
1. Lower Productivity
One of The main challenges of organic farming is its lower productivity compared To conventional methods. Organic farmers face greater difficulties in combating pests & diseases, which can lead To lower crop yields. This limitation may result in higher prices for organic produce & a smaller supply compared To conventionally grown food.
2. Higher Costs
Organic farming often requires more labor-intensive practices, such as manual weed control, crop rotation, & organic pest management. These additional efforts, along with The costs of organic certification, can make organic products more expensive for both farmers & consumers. The higher costs associated with organic farming can limit its accessibility To certain populations.
3. Limited Availability
While The demand for organic products has been increasing, The availability of organic food can still be limited in some areas. Organic farming requires specific conditions & certifications, & not all farmers are equipped or interested in transitioning To organic practices. As a result, consumers may have limited options when it comes To purchasing organic food.
The Pros of Conventional Farming
1. Higher Productivity & Efficiency
Conventional farming methods often employ The use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, & genetically modified organisms. These techniques can lead To higher crop yields, allowing farmers To produce more food efficiently. In conventional agriculture, advanced machinery & technologies are also utilized, further contributing To increased productivity.
2. Lower Costs & Affordability
The reliance on synthetic inputs in conventional farming can result in lower production costs compared To organic methods. This cost advantage often translates To more affordable food prices, making conventionally grown produce accessible To a wider range of consumers. The lower costs associated with conventional farming can also benefit farmers by increasing their profitability.
3. Greater Availability
Conventional farming methods are more widespread & adopted by a larger number of farmers globally. As a result, conventionally grown food is more readily available in supermarkets & grocery stores. This increased availability ensures a consistent food supply throughout The year, reducing The risk of shortages.
The Cons of Conventional Farming
1. Environmental Concerns
Conventional farming practices often rely heavily on synthetic fertilizers & pesticides, which can have negative impacts on The environment. These chemicals can leach into nearby water bodies, leading To water pollution. Additionally, The use of synthetic inputs can degrade soil health over time & contribute To The loss of biodiversity.
2. Food Safety Concerns
Conventional farming involves The use of synthetic pesticides & herbicides, which can leave residues on food. Prolonged exposure To these residues has been linked To potential health risks, including pesticide toxicity. Additionally, The routine use of antibiotics in livestock farming can contribute To The development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, posing risks To human health.
3. Animal Welfare Concerns
In conventional livestock farming, animals are often kept in confined spaces & subjected To intensive production systems. This can lead To compromised animal welfare, as they may not have adequate space To move or exhibit natural behaviors. The use of growth hormones & antibiotics in conventional livestock production is also a concern for animal welfare.
The Pros & Cons of Organic vs Conventional Farming: A Comparative Analysis
I have always been fascinated by The different approaches To farming & their impact on our environment & health. In this blog post, we will explore The pros & cons of organic farming compared To conventional farming. Both methods have their own merits & drawbacks, & it is important To understand The implications of each.
Environmental Impact
Organic farming is often celebrated for its positive environmental impact. Unlike conventional farming, organic practices prohibit The use of synthetic pesticides, herbicides, & genetically modified organisms (GMOs). This reduces The harmful chemical runoff into water sources & promotes biodiversity. Additionally, organic farming relies on natural fertilizers like compost & manure, which improve soil quality & decrease soil erosion.
However, critics argue that organic farming requires more land & resources compared To conventional farming, leading To potential deforestation & habitat destruction. It is essential To strike a balance between sustainable farming practices & meeting The increasing demands of a growing population.
To learn more about The environmental pros & cons of organic farming, check out this article.
Health & Nutrition
Organic farming is often associated with producing healthier & more nutritious food. Organic crops are grown without The use of synthetic pesticides & herbicides, reducing The risk of chemical residues on our food. Some studies suggest that organically grown fruits & vegetables may contain higher levels of certain nutrients & antioxidants.
However, The debate on The nutritional superiority of organic produce is still ongoing. Some researchers argue that The differences in nutrient content are minimal & may not significantly impact human health. It is important To note that consuming a varied & balanced diet rich in fruits & vegetables, regardless of their farming method, is key To maintaining good health.
Economic Considerations
Conventional farming is often praised for its ability To produce high yields, which can help meet The demands of a growing population. The use of synthetic fertilizers & pesticides allows for increased productivity & efficiency. This means that conventional farming can be more economically viable, providing food at lower costs.
On The other hand, organic farming can be financially challenging for farmers. The certification process is often costly, & The lower yields may result in higher prices for organic produce. However, consumer demand for organic food is growing, which presents economic opportunities for farmers who are willing To make The transition.
Comparison of Organic & Conventional Farming
| Organic Farming | Conventional Farming | |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Reduced chemical runoff, promotes biodiversity | Potential habitat destruction, intensive resource use |
| Health & Nutrition | Reduced chemical residues, potential higher nutrient content | Potentially comparable nutrient content |
| Economic Considerations | Higher production costs, growing consumer demand | Lower production costs, high yields |
Personal Experience
As someone who has dabbled in organic gardening, I have personally witnessed The rewards & challenges of growing food using organic methods. It requires more effort & attention To detail, but The satisfaction of harvesting pesticide-free produce makes it worthwhile. Organic farming not only benefits The environment but also contributes To a healthier lifestyle.
Conclusion
Both organic & conventional farming have their own advantages & disadvantages. While organic farming promotes environmental sustainability & may offer potential health benefits, it can be economically challenging. Conventional farming, on The other hand, allows for higher yields & lower production costs but has negative impacts on The environment & potential health risks associated with chemical residues. Ultimately, The choice between organic & conventional farming depends on balancing these different factors & striving for sustainable agriculture practices.

What is organic farming?
Organic farming is a method of agriculture that relies on natural processes & avoids The use of synthetic chemicals, pesticides, & genetically modified organisms. It emphasizes The importance of soil fertility, crop rotation, & biological pest control for sustainable & environmentally friendly food production.
What is conventional farming?
Conventional farming is a traditional method of agriculture that uses synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, & herbicides To maximize crop yield. It often involves monoculture, which means growing one type of crop over a large area, & relies on machinery & technological advancements for efficiency.
What are The pros of organic farming?
– Organic farming promotes soil health & fertility through The use of natural compost & organic matter.
– It reduces The risk of chemical residue on crops, leading To safer & healthier food.
– Organic farming encourages biodiversity by avoiding The use of synthetic pesticides, which can harm beneficial insects & animals.
– It helps To preserve water quality by prohibiting The use of synthetic fertilizers that can contribute To water pollution.
What are The cons of organic farming?
– Organic farming generally has lower crop yields compared To conventional farming methods, which can result in higher prices for organic produce.
– It requires more labor-intensive practices such as manual weeding & pest control.
– Organic farming may face challenges in meeting The growing demand for food due To limited land availability & lower productivity.
– The certification process for organic farming can be costly & time-consuming for farmers.
What are The pros of conventional farming?
– Conventional farming tends To have higher crop yields, allowing for a larger supply of affordable food.
– It can utilize advanced technology & machinery, leading To increased efficiency & productivity.
– Conventional farming methods often result in higher economic returns for farmers.
– The use of synthetic pesticides & fertilizers can effectively control pests & weeds, leading To higher crop quality.
What are The cons of conventional farming?
– Conventional farming practices can lead To soil erosion & degradation over time.
– The use of synthetic chemicals can have negative impacts on The environment, including water pollution & harm To wildlife.
– Conventional farming relies heavily on non-renewable resources such as fossil fuels for machinery & synthetic inputs.
– Consumers may be exposed To potential health risks due To The presence of pesticide residues on conventionally produced food.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when considering The pros & cons of organic vs conventional farming, it becomes clear that there are trade-offs associated with each method.
Organic farming offers numerous advantages such as healthier soil, reduced chemical exposure, & potentially higher nutrient content in foods. It also promotes biodiversity & supports a more sustainable ecosystem. However, it typically yields lower crop yields, resulting in higher prices for organic products & potentially limited availability.
Conventional farming, on The other hand, allows for higher yields, lower prices, & greater availability of crops. It often employs technological advancements that can increase efficiency & reduce post-harvest losses. However, it heavily relies on synthetic pesticides & fertilizers, which can have detrimental effects on The environment & human health.
Pros and Cons of Organic vs Conventional Farming
Ultimately, The choice between organic & conventional farming depends on various factors, such as personal preferences, environmental concerns, & economic considerations. It is crucial To strike a balance that minimizes harm To The environment while ensuring food security & affordability.
Moreover, it is important To recognize that both methods have room for improvement. Organic farming could benefit from advancements in technology & scientific research To increase yields, while conventional farming would benefit from adopting more sustainable practices To reduce environmental impacts.
In conclusion, The debate between organic & conventional farming is complex, & absolute conclusions cannot be drawn. It is essential To weigh The pros & cons of each method & consider The specific context in which farming practices are applied. By making informed choices & encouraging continuous improvements in both approaches, we can strive towards a more sustainable & environmentally-friendly agricultural system.