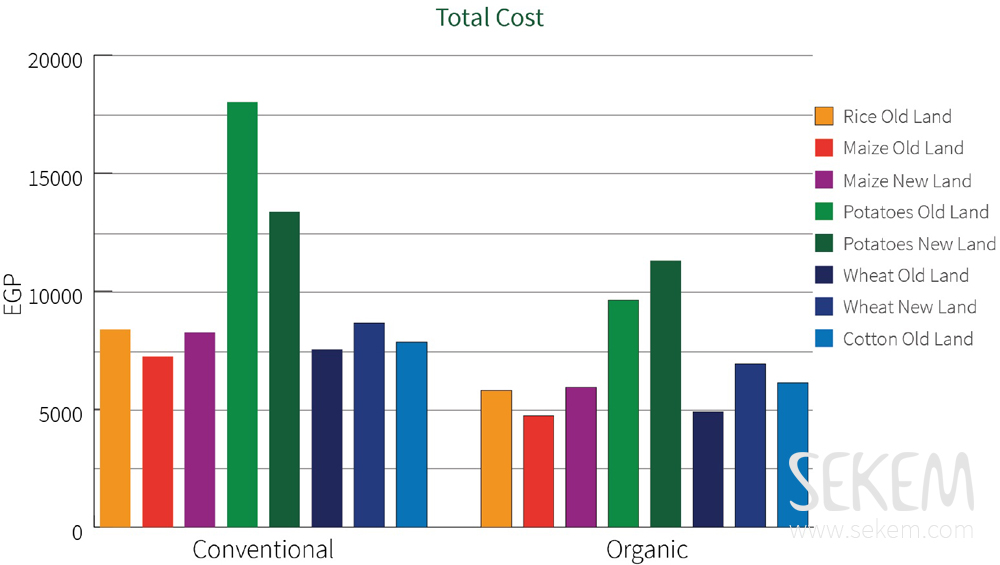
The cost of organic farming varies depending on various factors such as farm size, location, & The specific crops or livestock being raised. It typically involves higher initial investments in infrastructure, certification fees, & organic inputs. While organic farming may require more labor & time, it can result in higher profits due To premium prices for organic products. However, The financial benefits can take time To realize, making organic farming a long-term investment that requires careful planning & management.
How Much Does Organic Farming Truly Cost: A Realistic Financial Breakdown. Discover The true cost of organic farming with this realistic financial breakdown. Explore The affordability of sustainable agriculture in simple terms, without complex jargon. Understand The expenses involved in a conversational & human-friendly manner.
Understanding The True Costs of Organic Farming
Organic farming has gained significant popularity in recent years, with consumers increasingly seeking out organic produce. However, many people are still unsure about The true costs associated with organic farming. In this article, we will provide a realistic financial breakdown of organic farming, shedding light on The expenses involved & helping farmers make informed decisions.
The Current Landscape of Organic Farming
Before diving into The costs, let’s first take a look at The current state of organic farming. According To a study published by The USDA, despite The profit potential, organic field crop acreage remains relatively low in comparison To conventional farming. This indicates that there are certain barriers & challenges that organic farmers face, including financial considerations.
If you’re considering transitioning To organic farming, it’s crucial To be aware of these challenges & understand The financial implications involved. Organic farming requires adherence To strict regulations & certifications, which come at a cost. Additionally, organic farmers often invest more in labor & alternative pest control methods compared To conventional farmers.
Studies have shown that The price premium for organic products can offset some of these expenses. However, it’s essential To conduct a comprehensive analysis To ensure profitability in The long run.
Key Factors Affecting Organic Farming Costs
When analyzing The costs of organic farming, several factors come into play. Let’s explore these key aspects:
- Land & Equipment: Organic farmers often require larger land areas To implement crop rotation & maintain soil fertility. The costs of acquiring or leasing larger plots of land can significantly impact overall expenses. Moreover, investing in specialized organic farming equipment & machinery is often necessary, adding To The upfront costs.
- Seed & Supplies: Organic farmers need To source organic-certified seeds, fertilizers, & other inputs. These supplies can be more expensive than their conventional counterparts. However, it’s crucial To prioritize quality & source inputs from reputable suppliers To maintain The integrity of The organic farming process.
- Labor Expenses: Organic farming typically relies on manual labor for tasks such as weeding & pest control since synthetic pesticides & herbicides are not allowed. As a result, labor costs can be higher for organic farmers. Additionally, organic certification often requires more paperwork & record-keeping, increasing administrative tasks.
The Importance of Soil Health & Fertility
One of The fundamental principles of organic farming is maintaining soil health & fertility. Organic farmers focus on building & nourishing The soil through practices like crop rotation, cover cropping, & composting. These techniques promote biodiversity, enhance nutrient availability, & reduce The reliance on external inputs.
Investing in soil health & fertility is a long-term commitment but pays off in The form of healthier crops & improved yields. However, it’s important To note that rejuvenating degraded soil can require additional investments & time initially.
The High Costs of Organic Certification
Research has highlighted The significant costs associated with organic certification. Farmers must undergo regular inspections & comply with strict standards. These expenses can vary depending on The size of The farm & The type of certification required.
While organic certification allows farmers To command higher prices for their products, it’s vital To carefully analyze The return on investment. Smaller farmers may need To assess whether The certification costs outweigh The potential price premiums.
Access To Markets & Distribution Channels
Another aspect that influences The financial viability of organic farming is access To markets & distribution channels. Organic produce often commands a higher price, but reaching The right consumers & establishing reliable distribution networks can be challenging.
Farmers may need To invest in marketing strategies, participate in farmers’ markets or community-supported agriculture programs, & build relationships with local retailers or restaurants that value organic products. Moreover, transportation & storage costs may differ for organic produce due To The specific requirements for maintaining organic integrity.
Understanding The Costs of Organic Farming
Organic farming has gained immense popularity in recent years due To its environmental benefits & The growing demand for organic produce. However, many people are still unsure about The true costs of organic farming & whether it is a financially viable option. In this article, we will provide a realistic financial breakdown of The costs associated with organic farming, shedding light on The investments required & The potential returns.
The Initial Investment
Starting an organic farm requires a significant initial investment. This includes purchasing or leasing suitable land, acquiring organic seeds or seedlings, & investing in necessary farming equipment. The cost of land varies depending on location & size, but it is one of The most substantial expenses. Additionally, organic certification fees must be taken into account, as becoming a certified organic farm is essential for marketing organic products.
According To The California Certified Organic Farmers (CCOF), organic certification fees typically range from $400 To $3000 per year, depending on The certification agency & farm size. These fees cover The costs associated with inspection & certification processes.
Moreover, it is crucial To invest in high-quality organic seeds or seedlings, which may be more expensive than conventional options. Organic farming also requires specific equipment, such as tillers, tractors, irrigation systems, & pest control tools. The cost of these tools can vary significantly depending on The size of The farm & The region in which it operates.
Operational Costs
Once The initial investment is made, organic farms face ongoing operational costs. These include labor, water, fertilizers, pest control methods, & marketing expenses. Organic farming relies on manual labor for tasks such as planting, weeding, & harvesting. Therefore, labor costs can be higher compared To conventional farming methods that employ machinery for these tasks.
Water is another crucial resource in organic farming. Irrigation costs can vary depending on The availability of water sources & The efficiency of irrigation systems used. Many organic farmers implement drip irrigation systems, which can help reduce water consumption & costs.
Furthermore, organic fertilizers & pest control methods are typically more expensive than conventional options. Organic farmers avoid using synthetic fertilizers & chemicals, opting for natural alternatives. These alternatives may be more labor-intensive & require regular monitoring, increasing costs.
Market Considerations
When assessing The financial aspects of organic farming, it is essential To consider market factors. The demand for organic produce has been steadily increasing, but so has The competition. Organic farmers need To establish reliable distribution channels & marketing strategies To reach their target customers.
Different markets may offer varying prices for organic products, depending on factors such as location, consumer preferences, & competition. It is crucial for organic farmers To conduct thorough market research & analysis To determine The potential profitability of their products.
Comparing Organic Farming with Conventional Farming
To understand The true costs of organic farming, it can be helpful To compare it with conventional farming methods. While organic farming may require higher initial investments & operational costs, it offers several advantages over conventional farming.
Firstly, organic farming eliminates The use of synthetic pesticides, herbicides, & fertilizers, resulting in reduced environmental pollution & improved soil health. This contributes To The long-term sustainability of The farm, potentially reducing costs associated with soil degradation & chemical inputs.
Secondly, organic farming promotes biodiversity by supporting natural habitats & avoiding The use of genetically modified organisms (GMOs). This can lead To better pest control & increased resilience To climate change, reducing The need for expensive pest control measures.
Moreover, organic products often fetch premium prices in The market, which can offset The higher production costs. Consumers are willing To pay more for organic produce due To its perceived health & environmental benefits. However, it is crucial for organic farmers To establish efficient marketing strategies & distribution channels To capture this premium market.
| Factors | Organic Farming | Conventional Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Requires a significant investment in land, certification, & equipment | Relatively lower investment in land & equipment |
| Operational Costs | Higher labor, water, & pest control costs | Lower labor costs but higher synthetic inputs |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces pollution, preserves soil health, & promotes biodiversity | Potential negative impacts due To synthetic inputs |
| Market & Pricing | Potential for higher prices due To premium market demand | Pricing influenced by market factors & competition |
In conclusion, The costs of organic farming are higher compared To conventional farming methods, primarily due To The initial investment, operational expenses, & organic certification fees. However, organic farming offers numerous environmental benefits, potentially reducing long-term costs & promoting sustainability. Additionally, The growing demand for organic products can result in higher market prices, offsetting The increased production costs. Successful organic farmers must carefully manage expenses, establish efficient marketing strategies, & adapt To market dynamics To ensure profitability.
My Personal Experience with Organic Farming
As an organic farmer myself, I have experienced both The challenges & The rewards of this agricultural practice. The initial investment required To establish an organic farm was substantial, but I believe it was worth it considering The long-term benefits for The environment & our health.
Managing operational costs, such as labor & pest control, has been a continuous learning process. However, The satisfaction of producing healthy & nutritious food without relying on synthetic inputs is immeasurable. The demand for organic products in The market has been steadily growing, indicating that consumers value The quality & sustainability associated with organic farming.
Overall, while organic farming may involve higher costs, The positive impact it has on The environment & The potential for premium prices make it a viable & rewarding venture. It requires dedication, knowledge, & adaptability, but The benefits far outweigh The challenges.
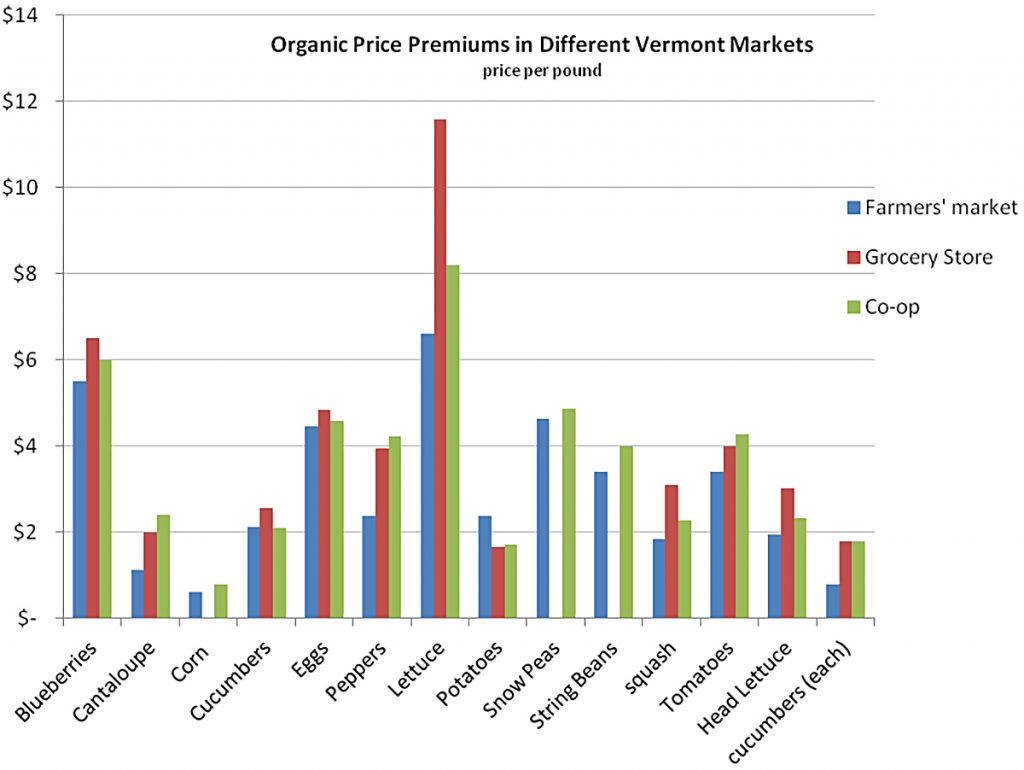
How much does organic farming truly cost?
Organic farming costs can vary depending on several factors such as farm size, location, & specific practices. In general, transitioning To organic farming methods may initially incur higher costs compared To conventional farming. This is primarily due To The necessary investments in organic fertilizers, pest management techniques, & The certification process.
What are The expenses involved in organic farming?
The expenses involved in organic farming can be categorized into different areas. These may include costs for organic seeds or seedlings, organic fertilizers & soil amendments, organic pest & weed control methods, labor, equipment, irrigation systems, & organic certification fees.
Are there any additional costs related To organic certification?
Yes, obtaining organic certification involves certain costs. These costs can vary depending on factors such as The certifying agency, farm size, & complexity of The farming operation. Certification fees typically cover application processing, inspections, & ongoing compliance monitoring.
How long does it take To recover The higher costs of organic farming?
The time it takes To recover The higher costs of organic farming can vary. It depends on factors such as crop yield, market prices, input costs, & farm management practices. While there may be an initial financial strain, transitioning To organic farming can lead To long-term benefits with improved soil health, reduced chemical inputs, & potential premium prices for organic products.
What financial resources or support are available for organic farmers?
There are various financial resources & support available for organic farmers. These may include government grants, loans, & subsidies specifically targeted towards organic farming. Additionally, there are organizations & agricultural institutions that offer education, training, & technical assistance To help farmers navigate The financial aspects of organic farming.
Can organic farming be financially viable in The long run?
Yes, organic farming can be financially viable in The long run. While The initial investment & higher costs may pose challenges, organic farming systems can provide sustainable & profitable opportunities. By building soil fertility, reducing input dependencies, & accessing premium organic markets, organic farmers can create a sustainable & financially stable business model.
Conclusion
In conclusion, organic farming is often seen as a more sustainable & environmentally friendly approach To agriculture. However, it is important To have a realistic financial breakdown when considering The true cost of organic farming.
When comparing organic farming To conventional methods, it is clear that there are additional expenses involved. These include The cost of certification, higher labor expenses, & The additional time required To manage organic practices. While these costs can be significant, it is important To consider The long-term benefits & potential profitability of organic farming.
Organic produce often commands a premium price in The market, as consumers are willing To pay more for food that is grown without The use of synthetic pesticides & fertilizers. This can help offset The higher costs associated with organic farming, potentially leading To higher profits in The long run.
It is also worth noting that The true cost of organic farming goes beyond financial considerations. Organic farming practices promote soil health & biodiversity, contribute To better water quality, & minimize The impact on The environment. These benefits are hard To quantify in monetary terms but are invaluable for The well-being of our planet.
While The financial cost of organic farming may be higher in The short term, it is an investment in a sustainable & ecologically sound future. By prioritizing soil health, biodiversity, & sustainable farming practices, organic farmers are contributing To The well-being of our planet & The health of consumers.
In conclusion, The true cost of organic farming should be evaluated holistically, taking into account financial considerations as well as The long-term environmental benefits. It may require more investment & effort, but organic farming offers a path towards a more sustainable & resilient agricultural system.