Exploring The Distinctions: A Comprehensive Guide To Organic & Conventional Farming Methods provides readers with a detailed comparison of The two most popular farming practices.
This comprehensive guide delves into The key distinctions between organic & conventional farming, including The use of synthetic pesticides, genetically modified organisms, & fertilizers. It explores The environmental impact, health benefits, & market demand for organic produce, as well as The yield, cost-effectiveness, & scalability of conventional farming methods. Whether you are a farmer, consumer, or simply interested in sustainable agriculture, this guide offers valuable insights into The complexities & choices within The farming industry.

Exploring the Distinctions: A Comprehensive Guide to Organic and Conventional Farming Methods. Discover The differences between organic & conventional farming methods in our comprehensive guide. Uncover The benefits & drawbacks of each approach in simple language without any unnecessary jargon. Explore this fascinating topic with us!
Understanding Organic & Conventional Farming Methods
In The world of agriculture, there are two primary farming methods that dominate The industry: organic farming & conventional farming. While both approaches aim To produce food & crops, they differ greatly in their practices & principles. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deeper into The distinctions between organic & conventional farming methods, exploring their benefits, drawbacks, & impact on The environment & human health.
Organic Farming: Going Back To Nature
Organic farming is an agricultural system that relies on natural processes & ecological balance To grow crops & raise livestock. Farmers who practice organic farming follow strict guidelines & regulations, ensuring that their methods align with The principles of sustainability & environmental stewardship. Here are some key aspects of organic farming:
1. No Synthetic Chemicals
One of The fundamental principles of organic farming is avoiding The use of synthetic chemicals such as pesticides, herbicides, & fertilizers. Instead, organic farmers rely on natural alternatives, including compost, manure, & biological pest control methods, To maintain soil fertility & manage pests effectively.
2. Soil Health is Paramount
Organic farmers prioritize The health & vitality of The soil. They employ various techniques, such as crop rotation, cover cropping, & The use of organic matter, To improve soil structure & fertility. By nurturing The soil, organic farming promotes biodiversity & enhances The overall health of The ecosystem.
3. Animal Welfare
Organic farming places a strong emphasis on animal welfare. Livestock raised organically are provided with ample space To move & graze freely. They are also given organic feed & are not subjected To hormones or antibiotics, ensuring that their products, such as milk & meat, are free from harmful residues.
Conventional Farming: Embracing Technological Advancements
Conventional farming, on The other hand, is a more industrialized approach To agriculture. It relies heavily on modern technology, synthetic inputs, & large-scale production methods To maximize yields. Here are some key aspects of conventional farming:
1. Intensive Chemical Usage
Unlike organic farming, conventional farming utilizes synthetic pesticides, herbicides, & fertilizers To control pests & enhance crop productivity. These chemicals help combat pests & weeds effectively but can have detrimental effects on The environment & human health if not used responsibly.
2. High-Yield & Monoculture
Conventional farming aims To produce high yields by focusing on monoculture, The practice of growing a single crop species in large quantities. Monoculture allows farmers To streamline production, increase efficiency, & meet The demands of a growing population. However, it can lead To soil degradation, nutrient depletion, & an increased risk of pest outbreaks.
3. Technological Advancements
Conventional farming embraces technological advancements, such as genetically modified organisms (GMOs), precision agriculture, & mechanization. These innovations help farmers optimize production, improve efficiency, & reduce labor requirements. However, critics argue that GMOs & certain technological interventions may have long-term ecological & health consequences that are yet To be fully understood.
The Impact on The Environment & Human Health
Both organic & conventional farming methods have significant implications for The environment & human health. Understanding these impacts can help consumers make informed choices about The food they consume. Here are some key considerations:
1. Environmental Sustainability
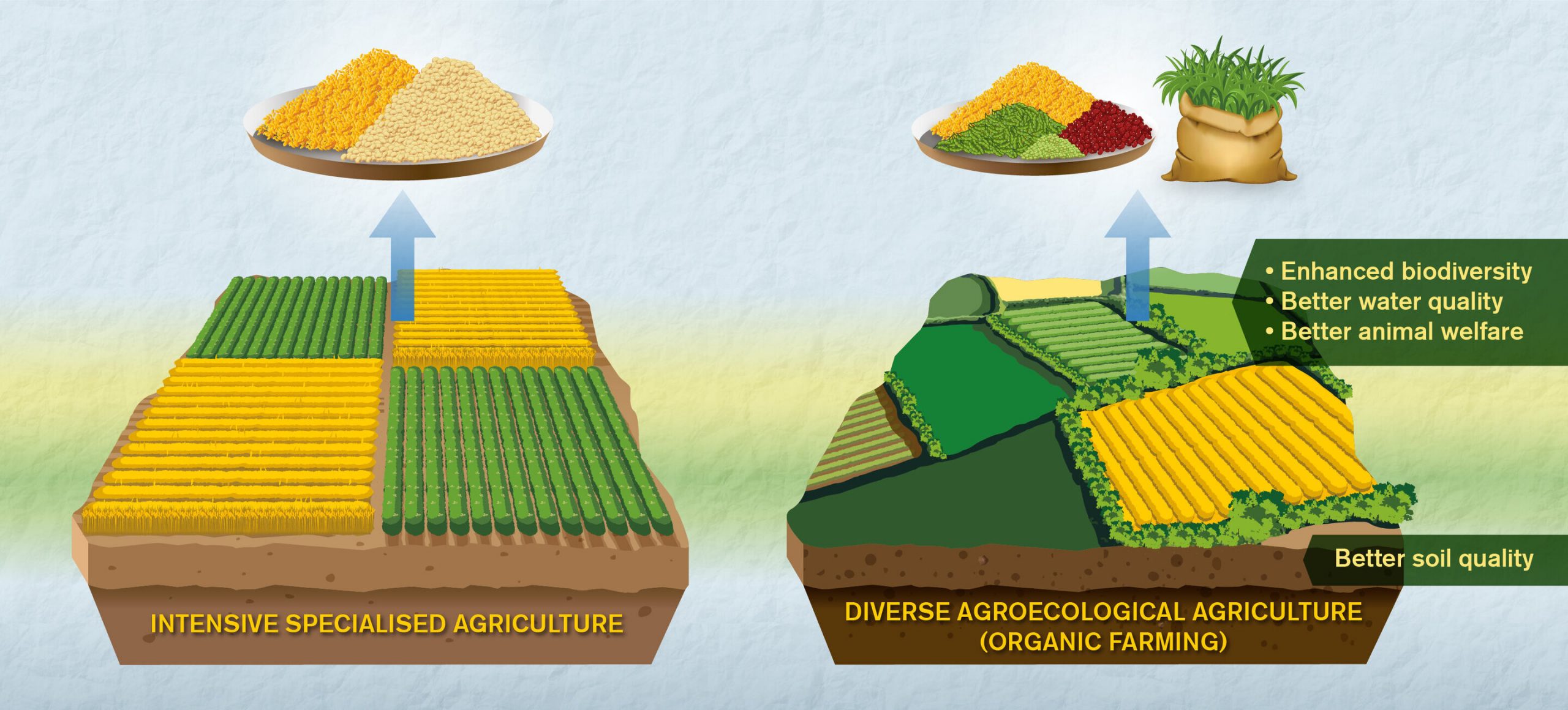
Organic farming, with its emphasis on biodiversity, soil health, & natural processes, supports The long-term sustainability of ecosystems. It reduces pollution, conserves water resources, promotes wildlife habitat, & minimizes The use of non-renewable resources. Conventional farming, while efficient in terms of yield, can result in soil erosion, water contamination, & biodiversity loss if not managed carefully.
2. Pesticide Residues
Organic farming avoids or minimizes The use of synthetic pesticides, reducing The risk of pesticide residues in food. In contrast, conventional farming may leave trace amounts of pesticides on fruits, vegetables, & other crops. However, it is important To note that The presence of pesticide residues in conventional produce is still well within safety limits set by regulatory authorities.
3. Nutritional Content
Studies comparing organic & conventional produce have yielded mixed results regarding their nutritional content. While some studies suggest that organic produce may contain higher levels of certain nutrients & antioxidants, others argue that The differences are minimal & not likely To have significant health impacts. Ultimately, a varied & balanced diet is key To obtaining essential nutrients, regardless of farming methods.

Guide to Organic and Conventional Farming
Organic & conventional farming are two distinct methods of agricultural production. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore The various distinctions between these two approaches, highlighting their key differences, benefits, & potential drawbacks. By understanding The nuances of organic & conventional farming methods, individuals can make informed decisions about The food they consume & support. So, let’s delve into The world of organic & conventional farming & explore The distinctions that set them apart.
Organic Farming
Organic farming is an agricultural method that prioritizes The use of natural inputs & sustainable practices. Unlike conventional farming, which heavily relies on synthetic fertilizers & pesticides, organic farming emphasizes The use of organic fertilizers, crop rotation, & biological pest control methods. This approach aims To minimize The use of synthetic chemicals & promote soil health, biodiversity, & overall ecological sustainability.
One of The key principles of organic farming is The prohibition of genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Organic farmers avoid using genetically engineered seeds & focus on preserving traditional crop varieties. This allows for The maintenance of genetic diversity & prevents potential risks associated with GMOs.
Additionally, organic farming promotes animal welfare by prohibiting The use of growth hormones & antibiotics in livestock production. Animals raised organically are provided with outdoor access, allowing them To engage in natural behaviors & live in healthier & more humane conditions.
Conventional Farming
Conventional farming, also known as industrial agriculture, is The dominant method of agricultural production worldwide. It relies heavily on synthetic inputs such as chemical fertilizers, pesticides, & herbicides. Conventional farmers use these inputs To maximize crop yields & combat pests & diseases that threaten their harvests.
While conventional farming often achieves high yields, it can have detrimental effects on The environment. The use of synthetic chemicals can contaminate soil & water sources, leading To negative consequences for ecosystems & human health. Additionally, conventional farming practices can contribute To The loss of biodiversity & The degradation of soil quality.
Conventional farming also allows for The use of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) in crop production. GMOs can be genetically engineered To exhibit specific traits, such as resistance To pests or herbicides. While genetically modified crops have been widely adopted, concerns remain regarding their long-term environmental & health impacts.
Comparing Organic & Conventional Farming
When comparing organic & conventional farming methods, several key distinctions arise. These distinctions involve farming practices, environmental impacts, human health considerations, & economic aspects. Let’s explore these differences in detail:
Farming Practices
Organic farming relies on natural inputs, such as compost, animal manure, & cover crops, To nourish The soil & provide nutrients To plants. In contrast, conventional farming relies on synthetic fertilizers & chemical inputs To achieve high crop yields. While organic farming follows a holistic & regenerative approach, conventional farming focuses on production efficiency & yield optimization.
Additionally, organic farming emphasizes crop rotation & integrated pest management techniques To control pests naturally, whereas conventional farming relies on synthetic pesticides & herbicides To combat pests & weeds.
It is important To note that transitioning from conventional To organic farming can be challenging for farmers, as it requires a shift in practices & potentially lower yields during The transition period. However, successful organic farming practices can lead To improved soil health & long-term sustainability.
Environmental Impacts
The environmental impacts of organic & conventional farming differ significantly. Organic farming practices prioritize soil health, biodiversity conservation, & ecological balance. Organic farms tend To have higher levels of beneficial insects, birds, & native plants, contributing To The overall health of ecosystems. By avoiding synthetic chemicals, organic farming also reduces The risk of harmful pesticide residues in The environment.
In contrast, conventional farming can have negative environmental consequences. The heavy use of synthetic fertilizers & pesticides can lead To water pollution, soil erosion, & The loss of biodiversity. Additionally, The carbon footprint of conventional farming is generally higher due To The energy-intensive production of synthetic inputs.
By choosing organic products, consumers can help support environmentally friendly farming practices & contribute To The preservation of ecosystems.
Human Health Considerations
Organic farming aims To prioritize human health by avoiding The use of synthetic chemicals in crop production. Organic foods are free from potentially harmful pesticide residues, providing consumers with a healthier alternative. Additionally, organic farming prohibits The use of growth hormones & antibiotics in livestock, reducing The risk of antibiotic resistance & promoting safer meat products.
Conventional farming, on The other hand, utilizes synthetic chemicals that can leave residues on crops & in The environment. Prolonged exposure To these chemicals may have adverse effects on human health, although strict regulations are in place To ensure that pesticide residues in food remain within acceptable limits.
While more research is needed To fully understand The long-term impacts of organic & conventional farming on human health, choosing organic products can be seen as a precautionary measure To minimize potential risks.
Economic Aspects
From an economic perspective, organic farming can be more labor-intensive & require higher upfront investments compared To conventional farming. This is due To The need for manual weed control, frequent crop monitoring, & The use of organic inputs, which can be more expensive than their synthetic counterparts.
Conventional farming, with its focus on efficiency & large-scale production, can often lead To lower costs & higher yields. However, it is important To consider The hidden costs associated with conventional farming, such as environmental damage, The loss of ecosystem services, & potential health impacts.
Furthermore, The market demand for organic products has been steadily increasing, providing opportunities for farmers To tap into premium markets & potentially earn higher profits.
Exploring The Distinctions Further
To further explore The distinctions between organic & conventional farming methods, it is essential To delve into detailed studies & research published on The topic. For a comprehensive understanding, we recommend referring To The following resources:
Study: A Comparative Analysis of Organic & Conventional Farming Methods
Resource: Organic versus Conventional Farming – An In-depth Comparison
By engaging with these resources, readers can access in-depth information & scientific findings that contribute To a holistic understanding of organic & conventional farming methods.
Guide to Organic and Conventional Farming
In conclusion, exploring The distinctions between organic & conventional farming methods sheds light on The various aspects that set them apart. From farming practices To environmental impacts, human health considerations, & economic aspects, it is evident that organic & conventional farming have significant differences. By understanding these distinctions, individuals can make informed choices when it comes To supporting sustainable & environmentally friendly agricultural practices.
Experience of Self
During my own exploration of organic & conventional farming methods, I have become increasingly aware of The importance of sustainable & environmentally friendly practices. Learning about The distinctions between these approaches has empowered me To make conscious decisions when purchasing food & supporting local farmers. By opting for organic products whenever possible & engaging in conversations surrounding sustainable agriculture, I feel more connected To The food I consume & The impact it has on our planet.

What are The differences between organic & conventional farming methods?
Organic farming relies on natural practices, avoiding synthetic chemicals, whereas conventional farming often utilizes pesticides & fertilizers.
How does organic farming contribute To environmental sustainability?
Organic farming practices promote biodiversity, reduce soil erosion, & minimize water pollution, making it more eco-friendly than conventional methods.
What are The main advantages of conventional farming?
Conventional farming allows for higher productivity due To The use of synthetic inputs, leading To increased crop yields & lower costs.
Does organic farming produce healthier food than conventional farming?
While no definitive scientific consensus exists, some studies suggest organic produce may contain higher levels of vitamins & antioxidants compared To conventionally grown counterparts.
Are organic farming methods more labor-intensive than conventional farming?
Organic farming often requires more hands-on management, such as manual weed control or compost application, which can increase labor requirements compared To conventional methods.
What certifications are required for organic farming?
Organic farms must meet specific criteria & obtain certification from authorized organizations, such as USDA Organic in The United States.
Are there any drawbacks To organic farming?
Organic farming can be more challenging & may yield lower crop quantities compared To conventional methods. However, this varies depending on factors such as location & crop types.
Can conventional farms transition To organic farming?
Yes, conventional farms can transition To organic by implementing organic practices & meeting The required criteria. The conversion process usually takes several years.
Which farming method is more cost-effective?
Conventional farming often has lower initial investment costs, but organic farming may yield higher profits in The long run due To The increasing demand for organic products.
How does consumer demand affect The farming industry?
With The rising consumer preference for organic products, farmers may consider transitioning To organic farming To meet The market demand & potentially increase their profitability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, exploring The distinctions between organic & conventional farming methods is essential in understanding The choices we make as consumers & The impact they have on our health & The environment. Throughout this comprehensive guide, we have seen that both methods have their strengths & weaknesses, & it ultimately comes down To personal preference & priorities.
Organic farming, with its emphasis on sustainability & avoiding synthetic chemicals, offers an alternative that is often seen as healthier for consumers & The environment. It promotes soil health, biodiversity, & animal welfare, while minimizing The use of pesticides & synthetic fertilizers. However, organic farming can sometimes be more expensive & yield lower crop yields.
On The other hand, conventional farming relies heavily on synthetic chemicals & genetically modified organisms (GMOs) To maximize crop productivity. This method often produces higher yields & lower costs, making it more accessible for many farmers. However, it also raises concerns about The long-term effects of pesticide use & The potential impacts on human health & The environment.
Ultimately, The choice between organic & conventional farming methods is a complex one. It depends on factors such as personal health priorities, environmental concerns, budget constraints, & availability of organic products. As consumers, it is important To be informed about The different farming practices & make choices that align with our values & priorities.
By understanding The distinctions between organic & conventional farming methods, we can make more informed decisions about The food we consume & support farming practices that align with our values. Whether it is choosing organic produce for its health & environmental benefits or supporting conventional farming for its cost-effectiveness & accessibility, The key is To make choices that contribute To a sustainable & healthy food system.