Organic farming differs from sustainable agriculture in its specific practices & regulations. While sustainable agriculture focuses on minimizing environmental impact & preserving natural resources, organic farming takes these principles a step further by using only natural inputs such as compost & avoiding synthetic pesticides & genetically modified organisms. Organic farming also requires specific certification & adheres To strict labeling rules, guaranteeing consumers that The products they buy are truly organic. This distinction sets organic farming apart from sustainable agriculture, ensuring a higher level of commitment To organic practices & consumer trust.

What Sets Organic Farming Apart from Sustainable Agriculture?. Discover The difference between organic farming & sustainable agriculture. Learn how these practices promote environmental stewardship & healthier food choices. Let’s explore The benefits & approaches that make them unique.
Understanding The Distinctions Between Organic Farming & Sustainable Agriculture
Organic farming & sustainable agriculture are two terms often used interchangeably, but they have distinct differences. While both practices aim To prioritize The health of The environment & provide healthier food options, their approaches & philosophies differ. In this article, we will explore what sets organic farming apart from sustainable agriculture & understand The unique characteristics of each.
Key Differences Between Organic Farming & Sustainable Agriculture
1. Certification
In organic farming, strict certification standards must be adhered To. These standards, set by various organizations such as The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), ensure that farming practices meet specific criteria regarding The use of synthetic pesticides, genetically modified organisms (GMOs), & synthetic fertilizers. On The other hand, sustainable agriculture doesn’t always require certification & focuses more on minimizing negative environmental impacts & promoting ecological balance.
2. Soil Management
Organic farming prioritizes soil health through practices such as crop rotation, composting, & The use of natural fertilizers. These techniques contribute To maintaining soil fertility & preventing soil erosion. Sustainable agriculture also emphasizes soil health but may incorporate a broader range of practices, including conventional methods that are modified To reduce environmental harm.
3. Pest & Weed Control
Organic farming relies on natural measures To control pests & weeds, such as beneficial insects, companion planting, & physical barriers. Synthetic pesticides are strictly limited. In sustainable agriculture, a combination of organic & conventional pest & weed control methods may be used, depending on The specific circumstances & goals of The farmer.
4. Genetic Modification
Organic farming prohibits The use of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) in any form. The focus is on natural & traditional breeding methods. In contrast, sustainable agriculture may allow The use of GMOs if they are proven To have positive ecological & social impacts.
5. Market Accessibility
Considering market accessibility, organic products often have a higher demand due To specific consumer preferences & certifications. Organic farmers can sell their products at premium prices, which can contribute To their economic sustainability. Sustainable agriculture, although it may involve environmentally-friendly practices, doesn’t necessarily carry The same premium price tag.
6. Environmental Impact
Both organic farming & sustainable agriculture strive To minimize environmental impact. However, organic farming places stronger emphasis on The reduction of synthetic inputs, ensuring biodiversity, & enhancing soil health. Sustainable agriculture takes a broader view, aiming To balance environmental impact with long-term economic viability & social equity.
The Need for Complementary Approaches
While organic farming & sustainable agriculture have their distinctions, it is important To note that they are not mutually exclusive. In fact, many farmers combine elements from both practices To create a holistic & sustainable approach tailored To their specific context.
Why I Believe in Sustainable Agriculture
As someone who has personally experienced The challenges & rewards of sustainable agriculture, I have witnessed The positive impact it can have on both The environment & local communities. By prioritizing ecological balance, sustainable agriculture ensures The long-term viability of our land & resources. It encourages biodiversity, minimizes pollution, & supports The well-being of rural communities. I firmly believe that sustainable agriculture is The path forward To build a healthier & more sustainable future.
The Distinction Between Organic Farming & Sustainable Agriculture
When it comes To agricultural practices, two terms that often come up are organic farming & sustainable agriculture. While these terms are sometimes used interchangeably, they actually have distinct differences. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed decisions about our food choices & farming practices.
Organic Farming: A Focus on Healthy Soil & Natural Inputs
Organic farming is an agricultural approach that prioritizes The use of natural inputs & The health of The soil. This method avoids The use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, & genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Instead, organic farmers rely on natural fertilizers, such as compost & manure, To nourish The soil & promote plant growth.
By avoiding The use of synthetic inputs, organic farming aims To minimize The negative impact on The environment & enhance The overall health of ecosystems. Organic farmers also prioritize biodiversity, allowing natural predators To control pests instead of relying on chemical interventions. This approach promotes long-term sustainability & The preservation of natural resources.
One of The key benefits of organic farming is The reduced exposure To harmful chemicals for farmers & consumers. Without The use of synthetic pesticides & fertilizers, organic produce can offer a healthier option for those concerned about The potential risks associated with chemical residues.
Sustainable Agriculture: A Holistic Approach To Long-Term Food Production
Sustainable agriculture, on The other hand, takes a more holistic approach To food production. It aims To balance environmental, social, & economic factors To ensure long-term viability. While organic farming is a component of sustainable agriculture, it is not The only focus.
Sustainable agriculture involves practices that minimize negative environmental impacts while also considering The social & economic aspects of food production. This approach takes into account soil health, water conservation, waste management, & biodiversity conservation. It also considers The well-being of farmers, farm workers, & surrounding communities.
In sustainable agriculture, farmers strive To implement diverse farming systems that are resilient To climate change & other challenges. This may include integrating organic practices, agroforestry, water conservation techniques, & precision farming technologies. The goal is To achieve a balance between productivity, environmental stewardship, & social responsibility.
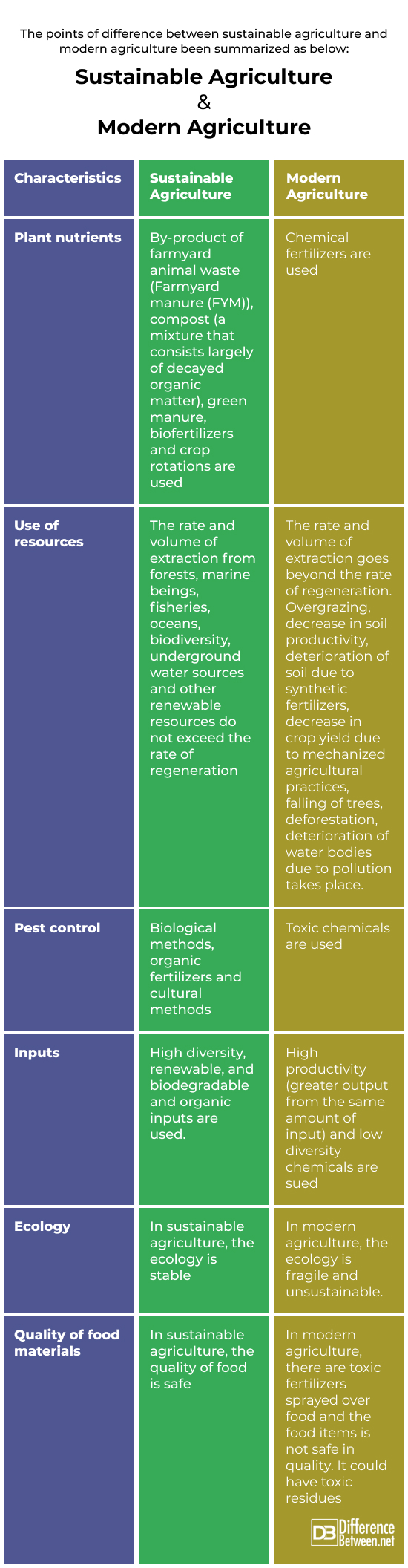
Comparing Organic Farming & Sustainable Agriculture
While organic farming & sustainable agriculture share some similarities, there are notable differences between The two. Organic farming is a specific subset of sustainable agriculture, focusing primarily on natural inputs & soil health. Sustainable agriculture encompasses a broader range of practices & considerations, including social & economic factors.
To further illustrate The distinctions between organic farming & sustainable agriculture, let’s compare them in a table:
| Aspect | Organic Farming | Sustainable Agriculture |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Primarily natural inputs & soil health | Holistic approach considering environmental, social, & economic factors |
| Focus | Minimizing synthetic inputs & supporting biodiversity | Balancing productivity, environmental stewardship, & social responsibility |
| Scope | Specific subset of sustainable agriculture | Broader range of practices & considerations |
As we can see, organic farming is an integral part of sustainable agriculture, but sustainable agriculture encompasses a wider array of practices & concerns.
The Importance of Choosing Sustainable & Organic Products
Now that we have a better understanding of organic farming & sustainable agriculture, it’s crucial To consider The importance of choosing sustainably & organically produced products. By opting for these products, we can support farming practices that prioritize The health of The environment, farmers, & consumers.
Purchasing organic products ensures that we are consuming food that is grown without synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, & GMOs. This can have a positive impact on our health & reduce The potential risks associated with chemical residues in conventionally grown produce.
Supporting sustainable agriculture goes beyond organic certification. It involves considering The entire lifecycle of The product, from The sourcing of raw materials To The packaging & transportation methods. By choosing products that are sustainably produced, we can contribute To The preservation of natural resources, reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, & support for fair labor practices.
In Conclusion
Understanding The differences between organic farming & sustainable agriculture allows us To make informed choices about The food we consume & The farming practices we support. While organic farming focuses on natural inputs & soil health, sustainable agriculture takes a broader approach, considering environmental, social, & economic factors. Both approaches are crucial for building a resilient & equitable food system.
Finally, from my own experience, I have witnessed The positive impacts of organic farming & sustainable agriculture on local communities. The adoption of these practices not only promotes healthier ecosystems but also empowers farmers To produce nutritious food while preserving The environment for future generations.
References:
1. Source
2. Source
3. Garden Worker
What sets organic farming apart from sustainable agriculture?
Organic farming & sustainable agriculture share many similarities, but they also have distinct differences. While both prioritize environmentally friendly practices, organic farming focuses primarily on using natural processes & materials, avoiding synthetic chemicals & genetic modification. On The other hand, sustainable agriculture encompasses a broader range of practices that aim To maintain long-term ecological balance, focusing on resource conservation, biodiversity, & community engagement. Both approaches are important for promoting a more sustainable & resilient food system.
Are organic farming & sustainable agriculture mutually exclusive?
No, organic farming & sustainable agriculture are not mutually exclusive. In fact, they often overlap & can complement each other. Many farmers practice organic farming within The framework of sustainable agriculture, incorporating both organic principles & sustainable practices. The goal is To achieve a balance between ecological health, economic viability, & social well-being. By adopting practices from both approaches, farmers can effectively meet The growing demand for organic products while also promoting sustainability.
What are The benefits of organic farming?
Organic farming offers several benefits over conventional farming methods. Firstly, it reduces The use of synthetic pesticides & fertilizers, thereby minimizing chemical pollution in The environment. Secondly, organic farming promotes soil health by improving its structure, fertility, & ability To retain water. Additionally, organic farming practices prioritize animal welfare & prohibit The use of hormones & antibiotics in livestock production. Lastly, organic farming encourages biodiversity, protecting ecosystems & preserving genetic diversity in crops.
How does sustainable agriculture promote environmental stewardship?
Sustainable agriculture promotes environmental stewardship by adopting practices that minimize The negative impact on natural resources. These practices include conserving water, reducing soil erosion, & preventing pollution of air & water. By minimizing reliance on agrochemicals, sustainable agriculture helps maintain The quality of soil & water, preserving The health of ecosystems. Furthermore, sustainable agriculture encourages The use of renewable energy sources, reducing greenhouse gas emissions & combatting climate change. Overall, sustainable agriculture aims To protect & enhance The environment for present & future generations.
Does organic farming contribute To food security?
Yes, organic farming can contribute To food security. By avoiding The use of synthetic chemicals, organic farming helps prevent soil degradation & water pollution, which can affect crop productivity. Organic farming also focuses on building healthy & fertile soil, enhancing its capacity To support plant growth & nutrient uptake. Additionally, organic farming practices often promote biodiversity, creating habitats for pollinators & natural pest control. By diversifying farming systems & improving soil health, organic farming can enhance resilience To climate change & contribute To long-term food security.
Conclusion
In conclusion, organic farming & sustainable agriculture are both holistic approaches To farming that prioritize The health of ecosystems & The well-being of farmers & consumers. However, there are key differences between The two.
Organic farming focuses on The use of natural methods & materials, avoiding The use of synthetic chemicals & genetically modified organisms. It places a strong emphasis on soil health, biodiversity, & The preservation of natural resources. By adhering To strict regulations & undergoing third-party certification, organic farmers provide consumers with a trustworthy & transparent option for food production.
Sustainable agriculture, on The other hand, encompasses a wider range of farming practices that prioritize environmental, economic, & social sustainability. While organic farming falls under The umbrella of sustainable agriculture, it is important To note that not all sustainable farming practices are necessarily organic.
What Sets Organic Farming Apart
The key distinction lies in The approach To inputs & methods. While organic farming strictly prohibits The use of synthetic chemicals, sustainable agriculture approaches The use of inputs more flexibly, considering alternatives that may also align with sustainable principles.
Both organic farming & sustainable agriculture offer solutions To The pressing challenges facing modern agriculture. By adopting these practices, we can promote healthier ecosystems, protect The health of farmers & consumers, & contribute To a more sustainable & resilient food system.
It is crucial for farmers, policymakers, & consumers To understand The differences between organic farming & sustainable agriculture & make informed choices when it comes To supporting & advocating for these practices. By working together, we can create a future where farming harmonizes with nature, promoting The well-being of all living beings & The planet.